Nowadays it is best to exercise caution when bringing the words “quantum” and “consciousness” anywhere near each other, lest you be suspected of mysticism or quackery. Eugene Wigner did not concern himself with this when he wrote his “Remarks on the Mind-Body Question” in 1967. (Perhaps he was emboldened by his recent Nobel prize for contributions to the mathematical foundations of quantum mechanics, which gave him not a little no-nonsense technical credibility.) The mind-body question he addresses is the full-blown philosophical question of “the relation of mind to body”, and he argues unapologetically that quantum mechanics has a great deal to say on the matter. The workhorse of his argument is a thought experiment that now goes by the name “Wigner’s Friend”. About fifty years later, Daniela Frauchiger and Renato Renner formulated another, more complex thought experiment to address related issues in the foundations of quantum theory. In this post, I’ll introduce Wigner’s goals and argument, and evaluate Frauchiger’s and Renner’s claims of its inadequacy, concluding that these are not completely fair, but that their thought experiment does do something interesting and distinct. Finally, I will describe a recent paper of my own, in which I formalize the Frauchiger-Renner argument in a way that illuminates its status and isolates the mathematical origin of their paradox.
* * *
Wigner takes a dualist view about the mind, that is, he believes it to be non-material. To him this represents the common-sense view, but is nevertheless a newly mainstream attitude. Indeed,
[until] not many years ago, the “existence” of a mind or soul would have been passionately denied by most physical scientists. The brilliant successes of mechanistic and, more generally, macroscopic physics and of chemistry overshadowed the obvious fact that thoughts, desires, and emotions are not made of matter, and it was nearly universally accepted among physical scientists that there is nothing besides matter.
He credits the advent of quantum mechanics with
the return, on the part of most physical scientists, to the spirit of Descartes’s “Cogito ergo sum”, which recognizes the thought, that is, the mind, as primary. [With] the creation of quantum mechanics, the concept of consciousness came to the fore again: it was not possible to formulate the laws of quantum mechanics in a fully consistent way without reference to the consciousness.
What Wigner has in mind here is that the standard presentation of quantum mechanics speaks of definite outcomes being obtained when an observer makes a measurement. Of course this is also true in classical physics. In quantum theory, however, the principles of linear evolution and superposition, together with the plausible assumption that mental phenomena correspond to physical phenomena in the brain, lead to situations in which there is no mechanism for such definite observations to arise. Thus there is a tension between the fact that we would like to ascribe particular observations to conscious agents and the fact that we would like to view these observations as corresponding to particular physical situations occurring in their brains.
Once we have convinced ourselves that, in light of quantum mechanics, mental phenomena must be considered on an equal footing with physical phenomena, we are faced with the question of how they interact. Wigner takes it for granted that “if certain physico-chemical conditions are satisfied, a consciousness, that is, the property of having sensations, arises.” Does the influence run the other way? Wigner claims that the “traditional answer” is that it does not, but argues that in fact such influence ought indeed to exist. (Indeed this, rather than technical investigation of the foundations of quantum mechanics, is the central theme of his essay.) The strongest support Wigner feels he can provide for this claim is simply “that we do not know of any phenomenon in which one subject is influenced by another without exerting an influence thereupon”. Here he recalls the interaction of light and matter, pointing out that while matter obviously affects light, the effects of light on matter (for example radiation pressure) are typically extremely small in magnitude, and might well have been missed entirely had they not been suggested by the theory.
Quantum mechanics provides us with a second argument, in the form of a demonstration of the inconsistency of several apparently reasonable assumptions about the physical, the mental, and the interaction between them. Wigner works, at least implicitly, within a model where there are two basic types of object: physical systems and consciousnesses. Some physical systems (those that are capable of instantiating the “certain physico-chemical conditions”) are what we might call mind-substrates. Each consciousness corresponds to a mind-substrate, and each mind-substrate corresponds to at most one consciousness. He considers three claims (this organization of his premises is not explicit in his essay):
1. Isolated physical systems evolve unitarily.
2. Each consciousness has a definite experience at all times.
3. Definite experiences correspond to pure states of mind-substrates, and arise for a consciousness exactly when the corresponding mind-substrate is in the corresponding pure state.
The first and second assumptions constrain the way the model treats physical and mental phenomena, respectively. Assumption 1 is often paraphrased as the `”completeness of quantum mechanics”, while Assumption 2 is a strong rejection of solipsism – the idea that only one’s own mind is sure to exist. Assumption 3 is an apparently reasonable assumption about the relation between mental and physical phenomena.
With this framework established, Wigner’s thought experiment, now typically known as Wigner’s Friend, is quite straightforward. Suppose that an observer, Alice (to name the friend), is able to perform a measurement of some physical quantity  of a particle, which may take two values,
of a particle, which may take two values, 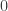 and
and 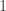 . Assumption 1 tells us that if Alice performs this measurement when the particle is in a superposition state, the joint system of Alice’s brain and the particle will end up in an entangled state. Now Alice’s mind-substrate is not in a pure state, so by Assumption 3 does not have a definite experience. This contradicts Assumption 2. Wigner’s proposed resolution to this paradox is that in fact Assumption 1 is incorrect, and that there is an influence of the mental on the physical, namely objective collapse or, as he puts it, that the “statistical element which, according to the orthodox theory, enters only if I make an observation enters equally if my friend does”.
. Assumption 1 tells us that if Alice performs this measurement when the particle is in a superposition state, the joint system of Alice’s brain and the particle will end up in an entangled state. Now Alice’s mind-substrate is not in a pure state, so by Assumption 3 does not have a definite experience. This contradicts Assumption 2. Wigner’s proposed resolution to this paradox is that in fact Assumption 1 is incorrect, and that there is an influence of the mental on the physical, namely objective collapse or, as he puts it, that the “statistical element which, according to the orthodox theory, enters only if I make an observation enters equally if my friend does”.
* * *
Decades after the publication of Wigner’s essay, Daniela Frauchiger and Renato Renner formulated a new thought experiment, involving observers making measurements of other observers, which they intended to remedy what they saw as a weakness in Wigner’s argument. In their words, “Wigner proposed an argument […] which should show that quantum mechanics cannot have unlimited validity”. In fact, they argue, Wigner’s argument does not succeed in doing so. They assert that Wigner’s paradox may be resolved simply by noting a difference in what each party knows. Whereas Wigner, describing the situation from the outside, does not initially know the result of his friend’s measurement, and therefore assigns the “absurd” entangled state to the joint system composed of both her body and the system she has measured, his friend herself is quite aware of what she has observed, and so assigns to the system either, but not both, of the states corresponding to definite measurement outcomes. “For this reason”, Frauchiger and Renner argue, “the Wigner’s Friend Paradox cannot be regarded as an argument that rules out quantum mechanics as a universally valid theory.”
This criticism strikes me as somewhat unfair to Wigner. In fact, Wigner’s objection to admitting two different states as equally valid descriptions is that the two states correspond to different sets of \textit{physical} properties of the joint system consisting of Alice and the system she measures. For Wigner, physical properties of physical systems are distinct from mental properties of consciousnesses. To engage in some light textual analysis, we can note that the word ‘conscious’, or ‘consciousness’, appears forty-one times in Wigner’s essay, and only once in Frauchiger and Renner’s, in the title of a cited paper. I have the impression that the authors pay inadequate attention to how explicitly Wigner takes a dualist position, including not just physical systems but also, and distinctly, consciousnesses in his ontology. Wigner’s argument does indeed achieve his goals, which are developed in the context of this strong dualism, and differ from the goals of Frauchiger and Renner, who appear not to share this philosophical stance, or at least do not commit fully to it.
Nonetheless, the thought experiment developed by Frauchiger and Renner does achieve something distinct and interesting. We can understand Wigner’s no-go theorem to be of the following form: “Within a model incorporating both mental and physical phenomena, a set of apparently reasonable conditions on how the model treats physical phenomena, mental phenomena, and their interaction cannot all be satisfied”. The Frauchiger-Renner thought experiment can be cast in the same form, with different choices about how to implement the model and which conditions to consider. The major difference in the model itself is that Frauchiger and Renner do not take consciousnesses to be entities in their own rights, but simply take some states of certain physical systems to correspond to conscious experiences. Within such a model, Wigner’s assumption that each mind has a single, definite conscious experience at all times seems far less natural than it did within his model, where consciousnesses are distinct entities from the physical systems that determine them. Thus Frauchiger and Renner need to weaken this assumption, which was so natural to Wigner. The weakening they choose is a sort of transitivity of theories of mind. In their words (Assumption C in their paper):
Suppose that agent A has established that “I am certain that agent A’, upon reasoning within the same theory as the one I am using, is certain that  at time
at time 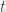 .” Then agent A can conclude that “I am certain that
.” Then agent A can conclude that “I am certain that  at time
at time 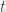 .”
.”
Just as Assumption 3 above was, for Wigner, a natural restriction on how a sensible theory ought to treat mental phenomena, this serves as Frauchiger’s and Renner’s proposed constraint. Just as Wigner designed a thought experiment that demonstrated the incompatibility of his assumption with an assumption of the universal applicability of unitary quantum mechanics to physical systems, so do Frauchiger and Renner.
* * *
In my recent paper “Reasoning across spacelike surfaces in the Frauchiger-Renner thought experiment”, I provide two closely related formalizations of the Frauchiger-Renner argument. These are motivated by a few observations:
1. Assumption C ought to make reference to the (possibly different) times at which agents 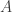 and
and 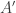 are certain about their respective judgments, since these states of knowledge change.
are certain about their respective judgments, since these states of knowledge change.
2. Since Frauchiger and Renner do not subscribe to Wigner’s strong dualism, an agent’s certainty about a given proposition, like any other mental state, corresponds within their implicit model to a physical state. Thus statements like “Alice knows that P” should be understood as statements about the state of some part of Alice’s brain. Conditional statements like “if upon measuring a quantity q Alice observes outcome  , she knows that P” should be understood as claims about the state of the composite system composed of the part of Alice’s brain responsible for knowing P and the part responsible for recording outcomes of the measurement of q.
, she knows that P” should be understood as claims about the state of the composite system composed of the part of Alice’s brain responsible for knowing P and the part responsible for recording outcomes of the measurement of q.
3. Because the causal structure of the protocol does not depend on the absolute times of each event, an external agent describing the protocol can choose various “spacelike surfaces”, corresponding to fixed times in different spacetime embeddings of the protocol (or to different inertial frames). There is no reason to privilege one of these surfaces over another, and so each of them should be assigned a quantum state. This may be viewed as an implementation of a relativistic principle.
After developing a mathematical framework based on these observations, I recast Frauchiger’s and Renner’s Assumption C in two ways: first, in terms of a claim about the validity of iterating the “relative state” construction that captures how conditional statements are interpreted in terms of quantum states; and second, in terms of a deductive rule that allows chaining of inferences within a system of quantum logic. By proving that these claims are false in the mathematical framework, I provide a more formal version of the no-go theorem. I also show that the first claim can be rescued if the relative state construction is allowed to be iterated only “along” a single spacelike surface, and the second if a deduction is only allowed to chain inferences “along” a single surface. In other words, the mental transitivity condition desired by Frauchiger and Renner can in fact be combined with universal physical applicability of unitary quantum mechanics, but only if we restrict our analysis to a single spacelike surface. Thus I hope that the analysis I offer provides some clarification of what precisely is going on in Frauchiger and Renner’s thought experiment, what it tells us about combining the physical and the mental in light of quantum mechanics, and how it relates to Wigner’s thought experiment.
* * *
In view of the fact that “Quantum theory cannot consistently describe the use of itself” has, at present, over five hundred citations, and “Remarks on the Mind-Body Question” over thirteen hundred, it seems fitting to close with a thought, cautionary or exultant, from Peter Schwenger’s book on asemic, that is meaningless, writing. He notes that
commentary endlessly extends language; it is in the service of an impossible quest to extract the last, the final, drop of meaning.
I provide no analysis of this claim.






























